- In addition to RC models and airsoft guns, you can also find microscopes, telescopes, metal detectors, chemistry kits, electronic kits and components, physics kits, technology kits and other hobby scientific products. The first of these stores has a very great inventory of electronic circuits and components.


EQUIPMENT FOR DETECTION OF RADIATION OR GASSES IN THE AIR
Geiger counters - radiation detectors
A geiger counter can be useful to detect and assess the radiation level in the surroundings. It is also useful to explore the geological composition in an area, to find special rock types and to investigate certain types of human activities.








MICROSCOPES







TELESCOPES




BINOCULARS AND BINOCULAR CAMERAS



NIGHT VISION SCOPES, BINOCULARS AND CAMERAS









METAL DETECTORS






Electronic kits and components - please go here
To find kits for experiments and learning about physics, chemistry, biology, electricity, magnetism and general sience - please click here
GOOD SOURCES OF ALL KIND OF HOBBY PRODUCTS
Two good general hobby stores
- In these stores you can find RC models of airplanes, boats, cars, drones, robots, tanks and construction mashines. You can also find a huge inventory of hobby guns. There are also magic kits and magic tricks.


Two good sources pf all kind of technical products, including telescopes, microscopes, cameras, camcorders, binoculars, Computers, cellphones, audio, video, gaming, components, software.
- These are big stores where you can find a lot of technical items for hobby and daily use, and many more special products for professional use. Among the products are: all kind of optical devices, rc models, computers. electronic components and experiment kits, home theaters, audio, video, cellphones, gaming, networking equipment, surveillance and security, automtion, office solutions, software, car electronics, tools for hobby and work.


INFORMATION ABOUT TELESCOPES
OPTICAL TELESCOPES
Generally
about optical telescopes
An optical telescope gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part
of the Electromagnetic spectrum (although some work in the infrared and
ultraviolet). Thereby also pictures of the objects that the light originates
from will be focused. Optical telescopes increase the apparent angular size
of distant objects, as well as their apparent brightness. Telescopes work by
employing one or more curved optical elements - lenses or mirrors - to
gather light or other electromagnetic radiation and bring that light or
radiation to a focus where the image can be observed, photographed or studied.
Practical telescopes have at least two main
lenses or lens collections. The objective resceives the light and focuses
it. The oculular or eyepiece enlarges the image of the object further. The
objective will make the image up- to down and right to left. To counteract
this effect, many telescopes have a third element between to convert back.
The focusing
can be done with convexe lenses, that is lenses that are thickest in the mid.
They can also be done by concave mirrors, that is mirrors that bulge inwards
at the side that collects the light. A combination of lenses and mirrors can
also be used.
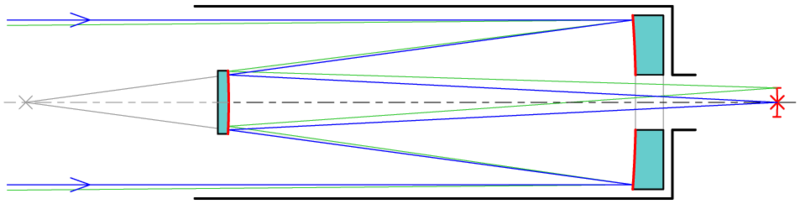
It is also possible to use mirrors to let the light go forth and back through the same
tube. In this way the telescope can be made a lot shorter. There are
three main types of telescopes.
The refracting telescope in which the light goes only through a collection
of lenses to be focused after having passed.
-
The reflecting telescope which uses only an arrangement of mirrors that
eventually reflects the light onto a plane.
-
The catadioptric telescope which uses a combination of mirrors and lenses.
Optical telescopes are used for astronomy and in many
non-astronomical instruments including theodolites, transits, spotting
scopes, monoculars, binoculars, camera lenses, and spyglasses.
Refractor
telescopes
A typical refractor has two basic
elements, a convex objective lens and an eyepiece lens. The objective in a
refracting telescope refracts or bends light at each end using lenses. This
refraction causes parallel light rays to converge at a focal point; while
those which were not parallel converge upon a focal plane. This can enable a
user to view the image of a distant object as if it were brighter, clearer,
and/or larger. Refracting telescopes can come in many different
configurations to correct for image orientation and types of aberration.
Galilean telescope
The original design Galileo came up
with is commonly called a Galilean telescope. It uses a convex objective
lens and a concave eyepiece lens.
The first telescope used the same principles that all telescopes would rely
upon. The combination of the two lenses gathered more light than the human
eye could collect on its own, focused it, and formed an image. Because the
image was formed by the bending of light, or refraction, these telescopes
came to be known as refracting telescopes or, simply, refractors.
Galileo’s best telescope magnified objects about 30 times. Because of flaws
in its design, such as the shape of the lens, the images were blurry and
distorted. But it was good enough for Galileo to explore the sky.
Keplerian Telescope
The Keplerian Telescope, invented by Johannes Kepler in 1611, is an
improvement on Galileo's design. It uses a convex lens as the eyepiece
instead of Galileo's concave one. The advantage of this arrangement is the
rays of light emerging from the eyepiece are converging. This allows for a
much wider field of view and greater eye relief but the image for the viewer
is inverted. Considerably higher magnifications can be reached with this
design but to overcome aberrations the simple objective lens needs to have a
very high f-ratio (Johannes Hevelius built one with a 45 m (150 ft.) focal
length). The design also allows for use of a micrometer at the focal plane
(used to determining the angular size and/or distance between objects
observed).
Achromatic telescope
The achromatic
refracting lens was invented in 1733 by an English barrister named Chester
Moore Hall although it was independently invented and patented by John
Dollond. The design limits the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration
by using an objective made of two pieces of glass (with different dispersion),
"crown" and "flint glass". Each side of each piece is ground and polished,
and then the two pieces are assembled together. Achromatic lenses are
corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus in
the same plane.